Unattended Access Overview
Introduction
Secure Remote Access enables IT administrators and vendors to access critical systems remotely while maintaining robust security and compliance. This topic introduces key terms such as unattended access, cloud gateways, on-premise gateways and the prerequisites for different configurations.
Subsequent topics cover getting started, product enrollment and modifying gateway configurations.
At the time of writing, Unattended Access is available to Windows and Mac clients. Access to Linux clients is expected later in 2026.
Related information
What is Unattended Access?
Unattended Access is a feature of Secure Remote Access that allows you to connect remotely to your servers and network endpoints directly from your browser, using a lot of the well-known Admin By Request features like: inventory, auditlog, settings and sub-settings, approval flows, integrations etc.
The implementation of Unattended Access can use either a "Cloud" or an "On-premise" gateway, eliminating the need for VPN and jump servers, while still maintaining a secure and segregated setup.
What is a cloud gateway?
A cloud gateway is an external (i.e. outside your network perimeter) cloud-based network access point that is centrally managed and securely routes traffic between users, cloud services, and internal resources. It acts as an intermediary, enforcing security policies, authentication, and traffic filtering while eliminating the need for traditional VPNs.
What is an on-premise gateway?
An on-premise gateway is an internal security appliance or software-based solution that enables secure, controlled access to internal corporate resources from external or remote locations.
Unlike a cloud gateway, an on-premise gateway resides within the organization's network perimeter, providing greater control over security, performance, and compliance.
Why deploy one?
An on-premise gateway is a good option if you already have one or more gateways in your environment.
Other common use cases for deploying an on-premise gateway:
-
Secure internal application access: Employees or third-party vendors need to securely access on-premise applications without exposing them to the internet.
-
Regulatory compliance: Organizations handling sensitive data (e.g., financial, healthcare, defense) must enforce strict security policies and data localization.
-
Air-gapped networks: Industries like defense, manufacturing, and critical infrastructure require isolated network access that avoids direct cloud exposure.
-
High-performance remote work: Low-latency access to local servers and applications for performance-critical tasks.
The following table summarizes the differences between the two gateway types.
|
Feature |
Cloud Gateway |
On-Premise Gateway |
|---|---|---|
|
Connectivity |
Traffic routed via cloud host’s global network |
Securely routes traffic within the internal network |
|
Data Storage |
Cloud-hosted |
Local/on-premise storage options |
|
Security Model |
Cloud-based security policies |
Local security enforcement with internal controls |
|
Network Dependency |
Relies on cloud host’s infrastructure |
Functions within LAN, can operate offline for local access |
|
Performance |
Cloud host-optimized |
Direct internal traffic routing, lower latency |
Prerequisites
In order to use the full power of Unattended Access, there are a number of prerequisites, listed under the following headings (not all are necessarily required - review those relevant to your environment):
 B. Data location
B. Data location
Your data is stored in a data center that is located in one of the geographic locations listed below. These are in Europe, the USA, the UK and Asia.
To determine your data location, go to page Tenant Settings > Data in the portal and click the RETENTION tab.
Note the geographic location shown in field Data Location - it will be one of the following:
-
EU West, Netherlands (Europe)
-
US East, Virginia (USA)
-
US West, California (USA)
-
London, United Kingdom (UK)
-
EU Central, Germany (Europe)
-
Singapore (Asia)
To determine the API prefix for your data center, go to page Settings > Tenant Settings > Data > API KEYS in the portal and check which API prefix is shown under About API Keys. The data center API URL (also known as the API prefix) will be one of the following:
-
https://dc1api.adminbyrequest.com (Europe - Netherlands)
-
https://dc2api.adminbyrequest.com (US East)
-
https://dc3api.adminbyrequest.com (UK)
-
https://dc4api.adminbyrequest.com (Europe - Germany)
-
https://dc5api.adminbyrequest.com (US West)
-
https://dc6api.adminbyrequest.com (Asia)
Make a note of your prefix - among other things, this is the domain used when an API Key is created.
You can also see your API prefix on the API web pages (e.g. Public API > Auditlog API). However, a small script runs in the background that determines to which data center you are attached, so JavaScript must be enabled in your browser for this to work.
 C. IP addresses and API URLs
C. IP addresses and API URLs
Admin By Request uses port 443 and the IP addresses and API URLs that need access through firewalls are as follows.
If your data is located in Europe (Netherlands):
-
IP: 104.45.17.196
-
DNS: api1.adminbyrequest.com
-
DNS: macapi1.adminbyrequest.com
If your data is located in the USA (East):
-
IP: 137.117.73.20
-
DNS: api2.adminbyrequest.com
-
DNS: macapi2.adminbyrequest.com
If your data is located in the UK:
-
IP: 85.210.211.164
-
DNS: api3.adminbyrequest.com
-
DNS: macapi3.adminbyrequest.com
If your data is located in Europe (Germany):
-
IP: 9.141.94.162
-
DNS: api4.adminbyrequest.com
-
DNS: macapi4.adminbyrequest.com
If your data is located in the USA (West):
-
IP: 172.184.188.29
-
DNS: api5.adminbyrequest.com
-
DNS: macapi5.adminbyrequest.com
If your data is located in Asia (Singapore):
-
IP: 52.230.54.129
-
DNS: api6.adminbyrequest.com
-
DNS: macapi6.adminbyrequest.com
Wherever you are, you can also use api.adminbyrequest.com, but the regional URLs will likely be more responsive.
 D. Cloud gateway (managed service)
D. Cloud gateway (managed service)
-
If you are using Secure Remote Access, you need to allow your browsers access to the following cloud gateways:
-
cloudgatewayeu1.accessbyrequest.com (Europe - Netherlands)
-
cloudgatewayus1.accessbyrequest.com (US East)
-
cloudgatewayuk1.accessbyrequest.com (UK)
-
cloudgatewaygermany1.accessbyrequest.com (Europe - Germany)
-
cloudgatewayuswest1.accessbyrequest.com (US West)
-
cloudgatewaysingapore1.accessbyrequest.com (Asia)
They are called over WSS (Websockets Secure) on port 443 from the browser.
Further, if you wish to remotely access endpoints using Unattended Access and Remote Support:
-
Outbound MQTT broker connectivity via Websockets - port 443 - for the following:
-
If your data is located in Europe (Netherlands):
Ten nodes (FastTrackHubEU1.azure-devices.net to FastTrackHubEU10.azure-devices.net) -
If your data is located in the USA (East):
Ten nodes (FastTrackHubUS1.azure-devices.net to FastTrackHubUS10.azure-devices.net) -
If your data is located in the UK:
Ten nodes (FastTrackHubUK1.azure-devices.net to FastTrackHubUK10.azure-devices.net) -
If your data is located in Europe (Germany):
Ten nodes (FastTrackHubGermany1.azure-devices.net to FastTrackHubGermany10.azure-devices.net) -
If your data is located in the USA (West):
Ten nodes (FastTrackHubUSWest1.azure-devices.net to FastTrackHubUSWest10.azure-devices.net) -
If your data is located in Asia:
Ten nodes (FastTrackHubSingapore1.azure-devices.net to FastTrackHubSingapore10.azure-devices.net)
-
-
For Unattended Access, RDP needs to be enabled on port 3389 on the device.
-
-
Cloudflare connectivity:
-
UDP outbound - port 7844 for the following:
-
region1.v2.argotunnel.com
-
region2.v2.argotunnel.com
-
If your firewall supports Server Name Indication (SNI), you need to allow the following URLs (UDP outbound - port 7844):
-
cftunnel.com
-
h2.cftunnel.com
-
quic.cftunnel.com
-
Refer to https://developers.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-one/connections/connect-networks/deploy-tunnels/tunnel-with-firewall/ for more information on Cloudflare's "tunnel with firewall" configuration.
-
-
The endpoint needs to be enrolled with an Admin By Request Secure Remote Access license (see Product Enrollment).
-
For Windows endpoints, RDP needs to be enabled on port 3389 on each device.
 E. On-premise gateway (self-hosted)
E. On-premise gateway (self-hosted)
-
Access to pull Docker images from adminbyrequest.azurecr.io
-
Admin By Request API - port 443 - for the following:
-
connectorapi1.adminbyrequest.com (if your data is located in Europe - Netherlands)
-
connectorapi2.adminbyrequest.com (if your data is located in the USA - East)
-
connectorapi3.adminbyrequest.com (if your data is located in the UK)
-
connectorapi4.adminbyrequest.com (if your data is located in Europe - Germany)
-
connectorapi5.adminbyrequest.com (if your data is located in the USA - West)
-
connectorapi6.adminbyrequest.com (if your data is located in Asia)
-
-
Outbound MQTT broker connectivity via Websockets - port 443 - for the following:
-
If your data is located in Europe (Netherlands):
Ten nodes (FastTrackHubEU1.azure-devices.net to FastTrackHubEU10.azure-devices.net) -
If your data is located in the USA (East):
Ten nodes (FastTrackHubUS1.azure-devices.net to FastTrackHubUS10.azure-devices.net) -
If your data is located in the UK:
Ten nodes (FastTrackHubUK1.azure-devices.net to FastTrackHubUK10.azure-devices.net) -
If your data is located in Europe (Germany):
Ten nodes (FastTrackHubGermany1.azure-devices.net to FastTrackHubGermany10.azure-devices.net) -
If your data is located in the USA (West):
Ten nodes (FastTrackHubUSWest1.azure-devices.net to FastTrackHubUSWest10.azure-devices.net) -
If your data is located in Asia:
Ten nodes (FastTrackHubSingapore1.azure-devices.net to FastTrackHubSingapore10.azure-devices.net)
-
-
Cloudflare connectivity:
-
UDP outbound - port 7844 for the following:
-
region1.v2.argotunnel.com
-
region2.v2.argotunnel.com
-
If your firewall supports Server Name Indication (SNI), you need to allow the following URLs (UDP outbound - port 7844):
-
cftunnel.com
-
h2.cftunnel.com
-
quic.cftunnel.com
-
Refer to https://developers.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-one/connections/connect-networks/deploy-tunnels/tunnel-with-firewall/ for more information on Cloudflare's "tunnel with firewall" configuration.
-
-
In order for the on-premise gateway to be able to discover devices on the network, these need to be available to the gateway on ports 3389 (RDP), 22 (SSH) or 5900/5901 (VNC).
 F. Vendor Access
F. Vendor Access
A further prerequisite applies to Vendor Access, where SSO must be enabled for each user who will login to the Vendor Access page (https://access.work).
How does Unattended Access work?
Architecture
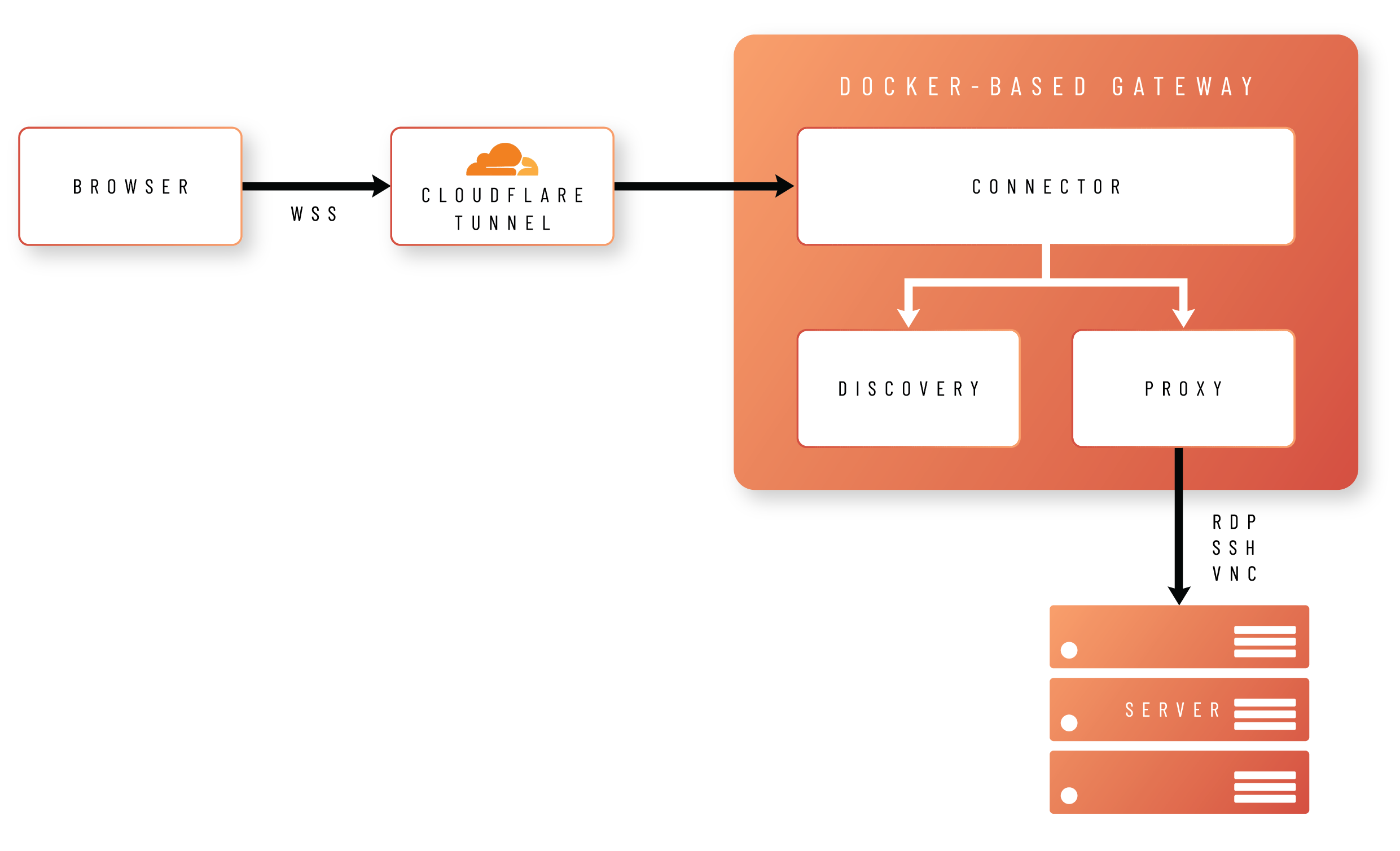
The idea behind Unattended Access is to allow users to connect to your remote endpoints using nothing but their browsers.
In order to achieve this, the browser creates a Secure WebSocket connection to a Docker-based gateway, hosted either in your own infrastructure (self-hosted) or as a managed service.
The gateway comprises three different images:
-
Connector
Handles validation and translation of the data between the portal and the proxy container, as well as managing logs, health checks and other data. -
Proxy
Establishes a protocol connection between Admin By Request and your endpoint using either RDP, SSH or VNC. -
Discovery
Handles automatic discovery of connectable devices running on the same network as the gateway.
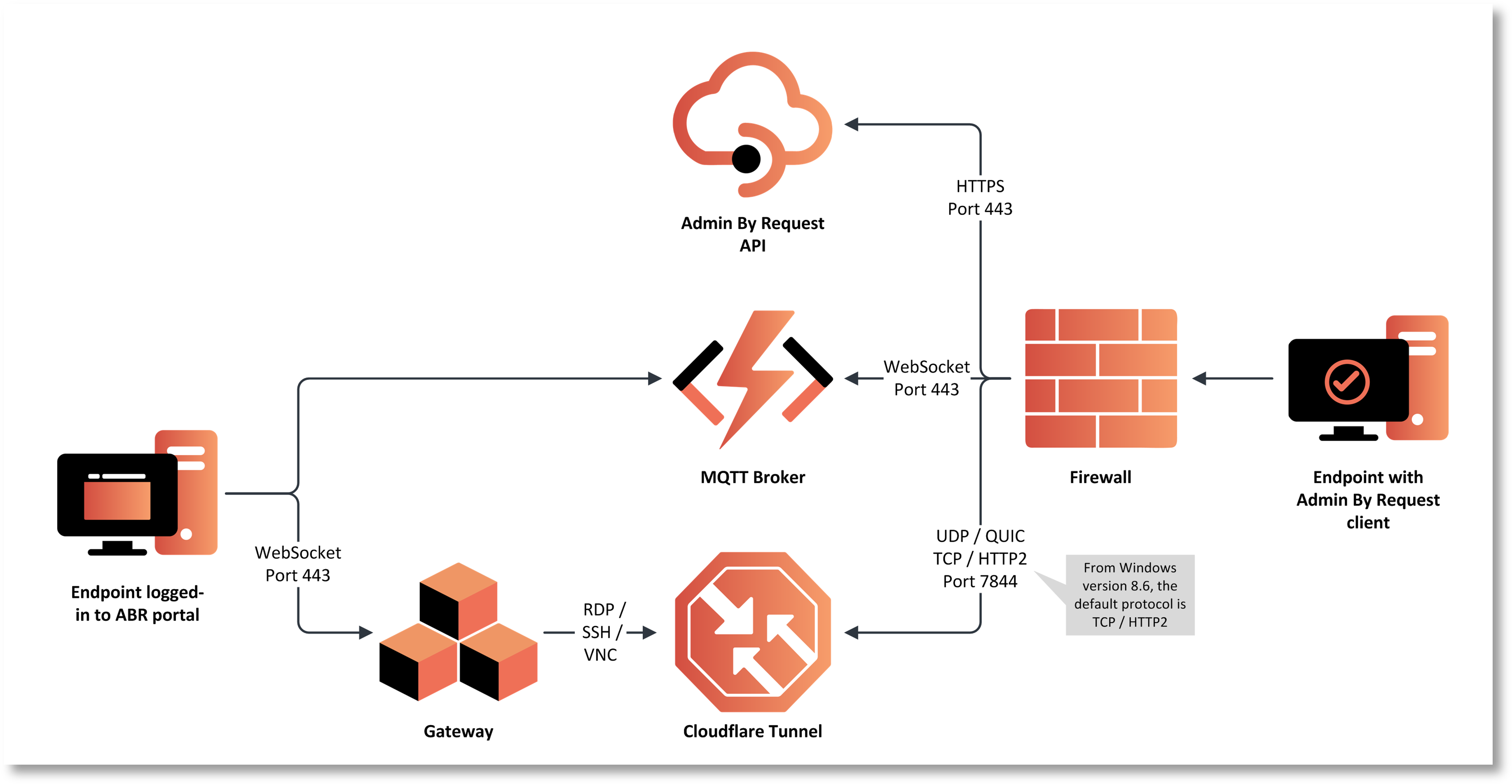
Process
The process by which a user establishes an unattended access session is:
-
The user initiates a connection from the Admin By Request Portal.
-
The Admin By Request client on the unattended endpoint receives an instruction from the MQTT Broker to fetch settings using the Admin By Request API.
-
The settings response instructs the Admin By Request client to open a Cloudflare Tunnel by making an outbound UDP call on port 7844 using the QUIC Protocol.
-
The Gateway is instructed to forward the RDP, SSH or VNC connection through the tunnel opened by the endpoint.
-
A secure WebSocket connection is established between the user's browser and the Gateway. The response stream from the RDP, SSH or VNC connection is routed back to the browser using this secure connection.
The process is illustrated in the following diagram:
macOS behavior and limitations
-
On macOS, unattended sessions use a just-in-time VNC path rather than RDP - this means it’s important to note that the screen of the device being remotely connected to can be observed and interacted with by anyone with physical access to the Mac.
-
Passwordless sign-in is not currently available for macOS unattended workflows - this capability is scheduled for a future release (during 2026).
-
When the remote operator connects, the session lands on the login screen and requires valid endpoint credentials - there is no network-level authentication, meaning that, with Unattended Access, the user will end up at the login screen and will have to log in with a local account or a Break Glass account. Furthermore, if a user is already signed in on the device, he/she will be prompted to log out before a connection can be made (same as on RDP). For a step-by-step example of this, refer to Connecting to a Mac.
-
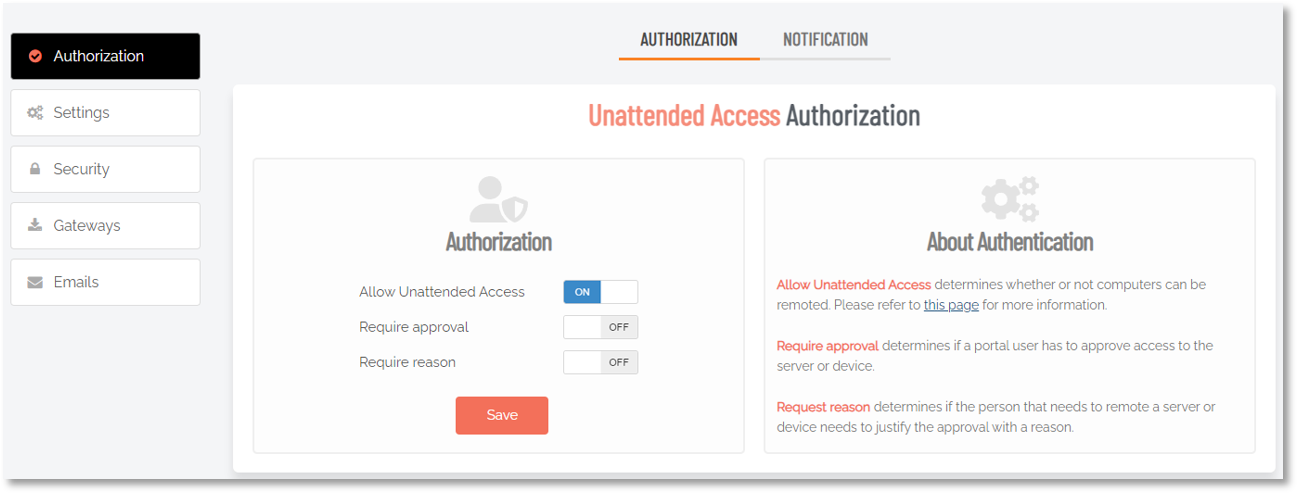
The Mac client supports an Unattended Remote Support mode - be aware that this basically starts a remote support session that doesn’t require user interaction. Useful for something like Kiosk devices for example. The setting is OFF by default and there is a warning in the portal attached to it:

What next?
As well as outlining how to get started with Unattended Access, this
The next section covers licensing endpoints for Secure Remote Access via Product Enrollment. After that, Getting Started lists the initial steps for enabling Unattended Access, followed by the steps required for a managed cloud service, and then the steps required for a self-hosted implementation.